Lemmy stalinists are going to enjoy this one
- 17 Posts
- 79 Comments

 19·2 months ago
19·2 months agoUrr, I don’t think that’s it. I’m not sure stereo sound for vinyls has ever worked so that something like this would be necessary, and it wouldn’t really make sense – why would they have to put vocals on one channel and instruments on the other?
A stereo vinyl player just has the needle moving up and down in addition to left and right, so that the left-right axis is the sum of the waveforms of both channels and the up-down axis is the difference – which means that a regular mono player can play stereo vinyls

 7·2 months ago
7·2 months ago… what
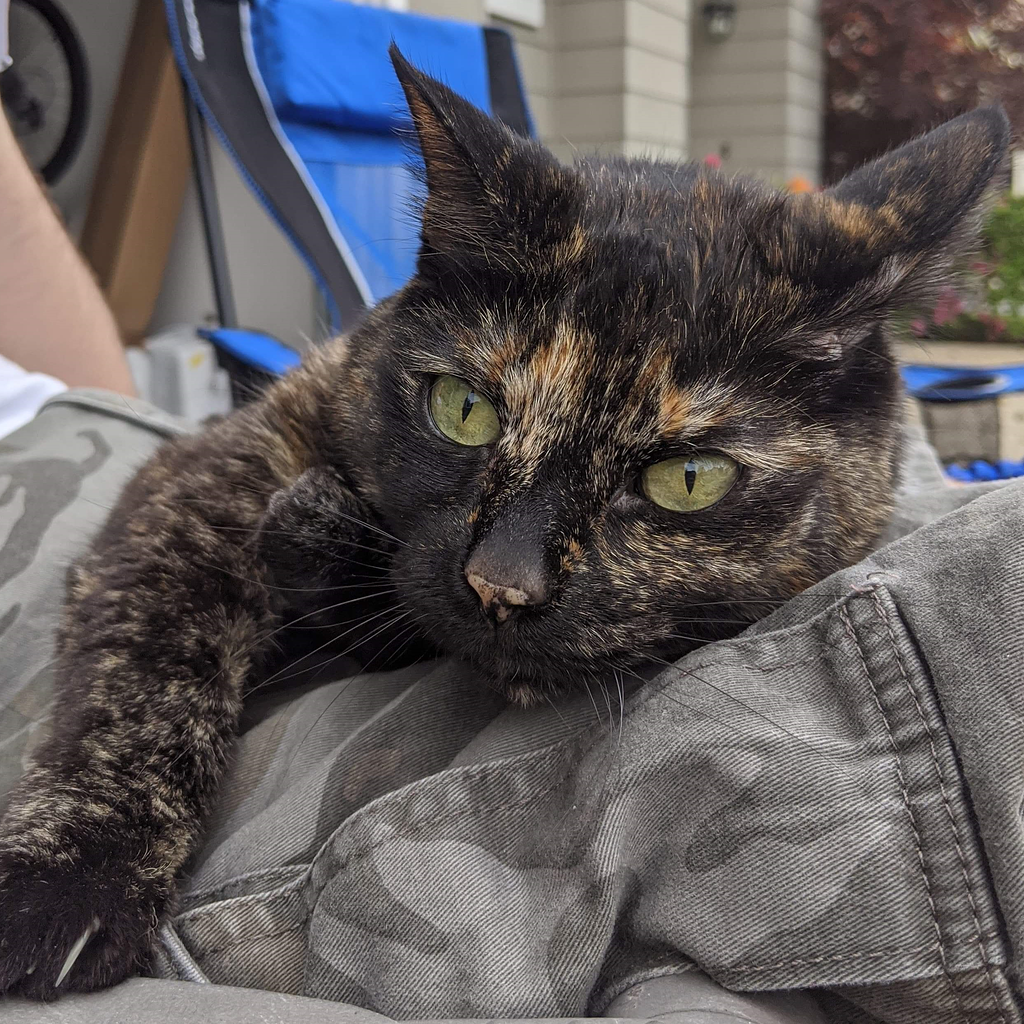
 21·2 months ago
21·2 months agoIf OP’s not from the US, turkey might not be an option – it’s not very common in a lot of places here in Europe for example.
Might be an option to just buy cat food (after they recover from their injury) and hide it in their room if the stepmom is that controlling

 31·2 months ago
31·2 months agoGah, honestly I’m not surprised at all she’s like that, she sounds exactly like the type.

 151·2 months ago
151·2 months agoHoly crap, that’s sounds outright abusive
That’s known as a ligature and they’re pretty common in many programming-oriented fonts, which usually have stylistic sets with different ligatures for different programming languages that you can optionally enable in your editor’s configuration. For example, here’s the stylistic sets the Monaspace font offers:
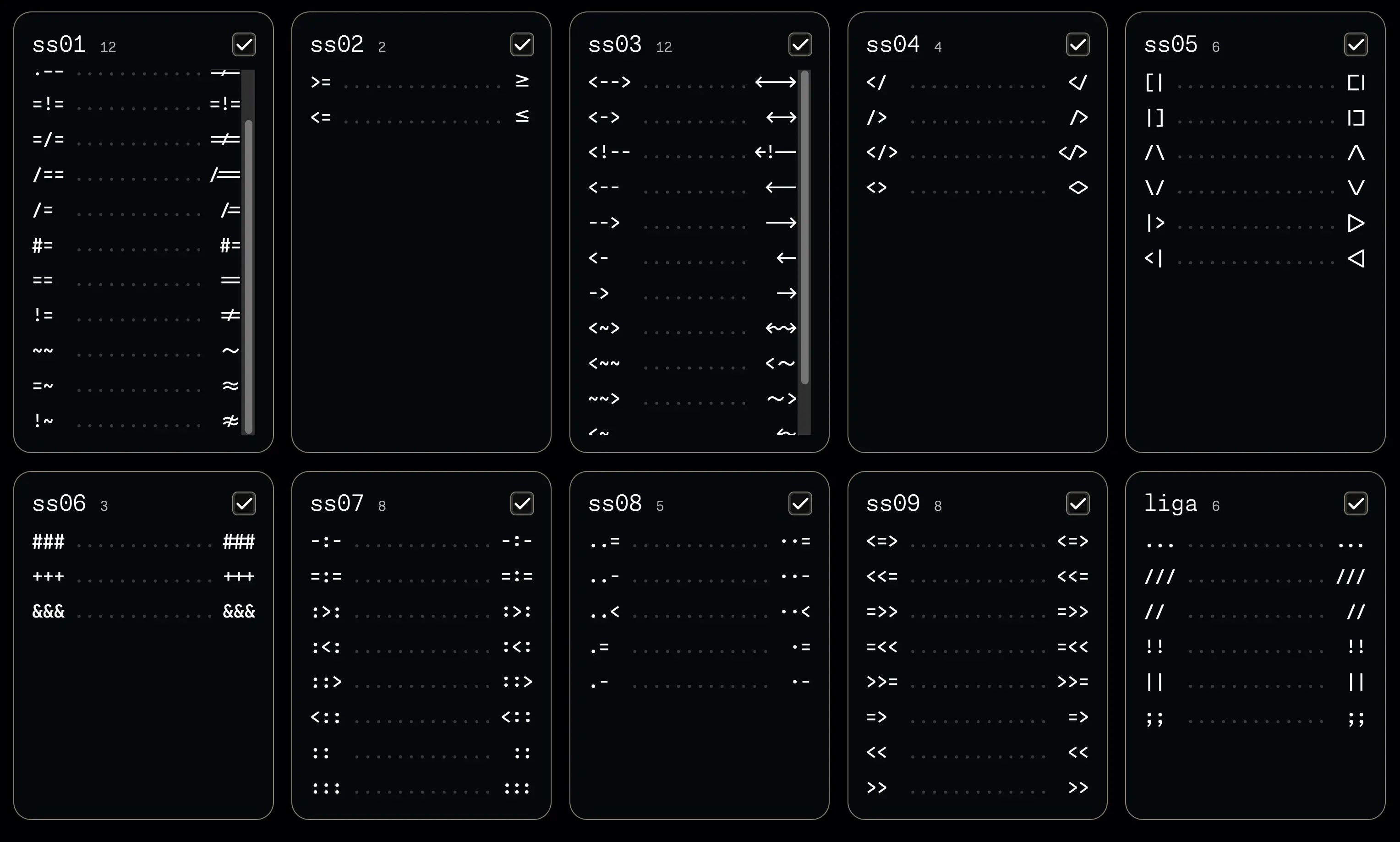
Personally I’m not too fond of ligatures so I never enable any, but many folks do like them.
Edit: and just as a side note, ligatures are super common in many fonts, you just might not notice them. Here’s some classic examples from the DejaVu Serif font, with and without a ligature:

"A".reverse() == "∀"Where is your god now?!

 5·2 months ago
5·2 months agoMore of a tragicomedy, really
Where’s your sense of adventure?!
Calling
reverse()on a function should return its inverse
You’re no fun
Use a dynamically typed language and you won’t have to: just override the default
reverse()method on strings like a Real Programmer!Unintended consequences you say? Nonsense! What could possibly go wrong?
"E".reverse() == "∃"
I dint know many OO languages that don’t have a useless toString on string types.
Well, that’s just going to be one of those “it is what it is” things in an OO language if your base class has a
toString()-equivalent. Sure, it’s probably useless for a string, but if everything’s an object and inherits from some top-levelObjectclass with atoString()method, then you’re going to get atoString()method in strings too. You’re going to get atoString()in everything; in JS even functions have atoString()(the output of which depends on the implementation):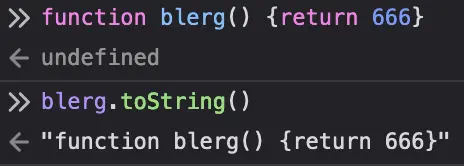
In a dynamically typed language, if you know that everything can be turned into a string with
toString()(or the like), then you can just call that method on any value you have and not have to worry about whether it’ll hurl at runtime because eg.Strings don’t have atoStringbecause it’d technically be useless.
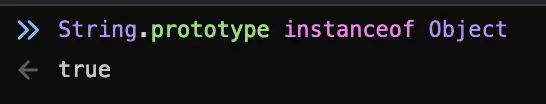
Everything that’s an
Objectis going to either inheritObject.prototype.toString()(mdn) or provide its own implementation. Like I said in another comment, even functions have atoString()because they’re also objects.A
Stringis anObject, so it’s going to have atoString()method. It doesn’t inheritObject’s implementation, but provides one that’s sort of a no-op / identity function but not quite.So, the thing is that when you say
const someString = "test string", you’re not actually creating a newStringobject instance and assigning it tosomeString, you’re creating astring(lowercases!) primitive and assigning it tosomeString: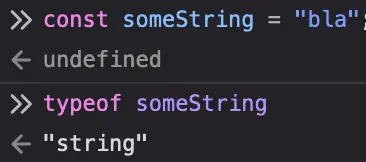
Compare this with creating a
new String("bla"):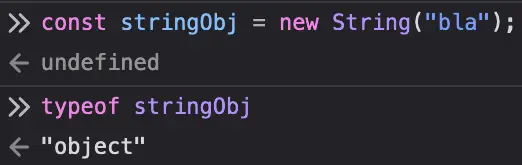
In Javascript, primitives don’t actually have any properties or methods, so when you call
someString.toString()(or call any other method or access any property onsomeString), what happens is thatsomeStringis coerced into aStringinstance, and thentoString()is called on that. Essentially it’s like goingnew String(someString).toString().Now, what
String.prototype.toString()(mdn) does is it returns the underlyingstringprimitive and not theStringinstance itself: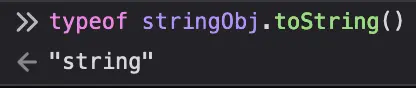
Why? Fuckin beats me, I honestly can’t remember what the point of returning the primitive instead of the
Stringinstance is because I haven’t been elbow-deep in Javascript in years, but regardless this is whatString’stoString()does. Probably has something to do with coercion logic.
This is absolutely true, but it still seems to me that we’re throwing the baby out with the bath water when we just stick to extremely terse symbols for everything regardless of context.
Reading articles would be so much easier if they used even slightly longer names – thankfully more and more computer science articles do tend to use more human readable naming nowadays, at least.
Sure, longer names make manipulation harder a bit more annoying if you’re doing it by hand, but if you do need to manipulate something you can then abbreviate the terms (and I’m 60% sure I’ve seen some papers that had both a longer form and a shorter form for terms, so one for explaining shit and one for the fiddly formal stuff)
Of course using terse terms is totally fine when it’s clear from the context what eg. ∆x means.
Ah, I managed to completely miss the last part of the comment because I’m an eejit who can’t read good
In 2017 his name was mentioned as a visionary comparable to the Wright Brothers and Zefram Cochrane (inventor of the warp drive) on a Star Trek episode set in the 2250s.
By a character who was explicitly evil and whose judgement we were not meant to trust, though




Surprisingly few downvotes so far.